Migrating from on-premise systems to cloud computing can be a daunting task for many businesses, but it doesn't have to be.
While the process requires careful planning and dedicated resources, following an appropriate strategy and considering any potential challenges can help make sure the project is successful.
In this blog post, we'll explore how to successfully migrate from your existing on-premises system to cloud computing, looking at steps you should take before, during, and after migration, common challenges companies encounter along the way, as well as different strategies that can help alleviate these problems.
So, stick around because if you're wondering how to make your move safely while maintaining maximum efficiency during the transition period — then you won't want to miss out!
Editor's Note: This blog post is last updated in Aug 2024.
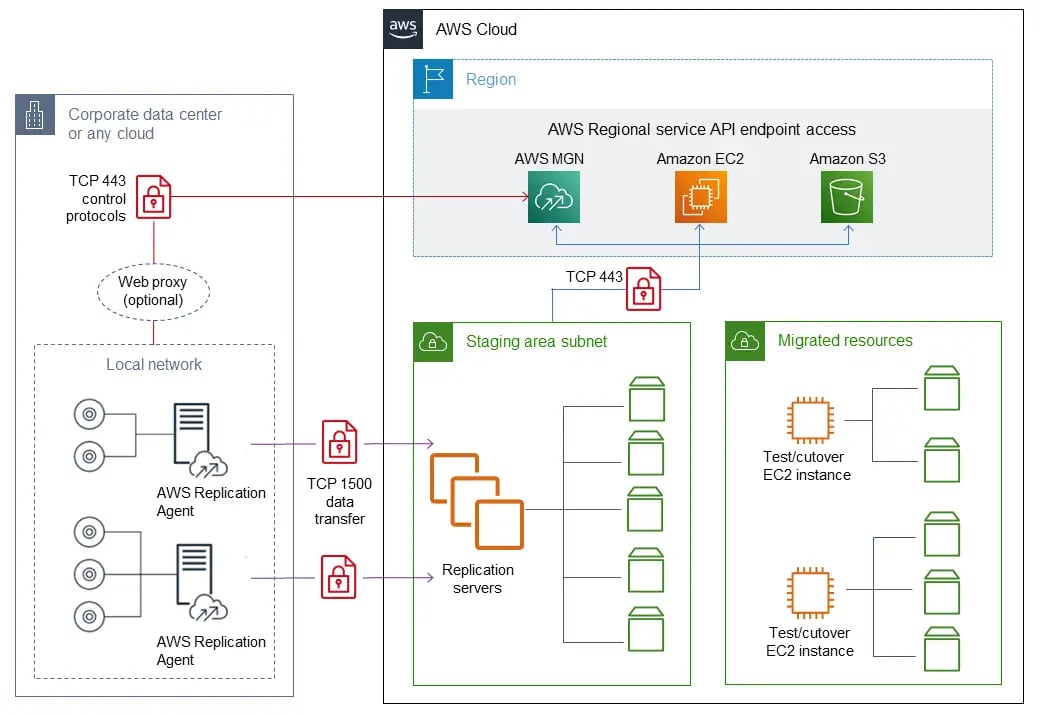
On premise to cloud migration
On-premise to cloud migration is the process of transferring an organisation's data, applications, and digital assets to cloud-based servers.
This migration allows companies to store information off-site, making it accessible from anywhere in the world, reducing the costs associated with maintaining physical servers and personnel to manage them.
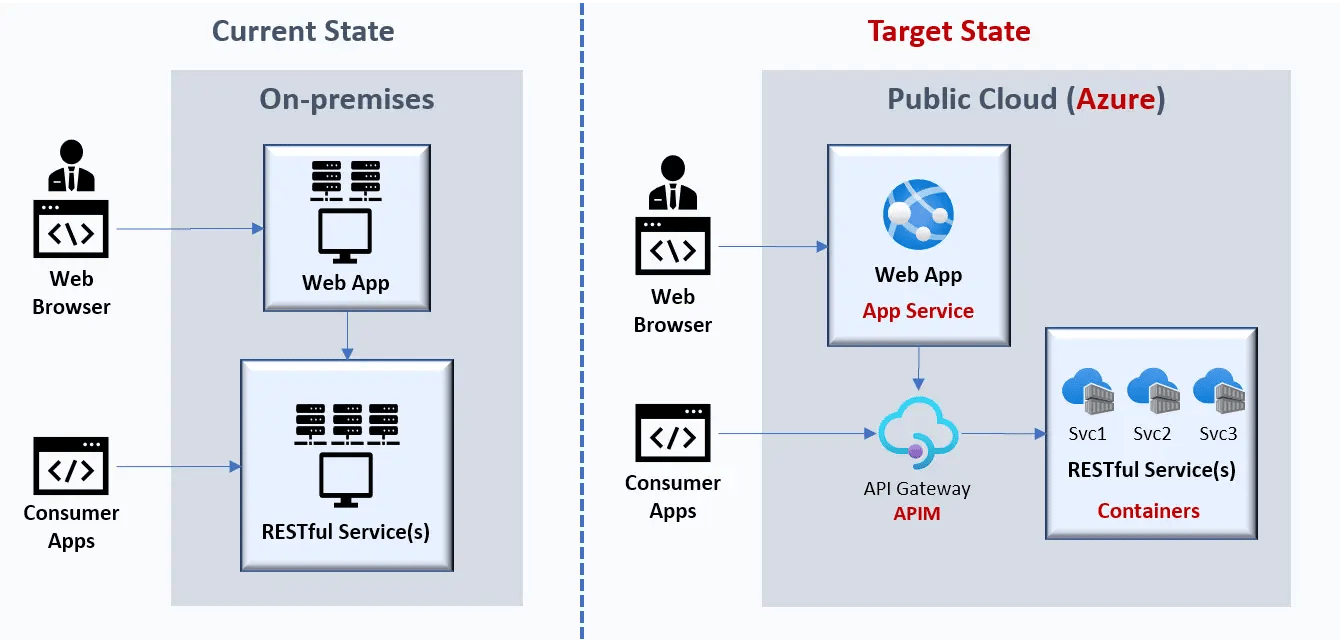
With on-premise to cloud migration, companies can benefit from cloud-based services, including improved scalability, reliability, and security, making it easier for companies to focus on their core business objectives.
Types of Cloud Migration Strategies
According to Gartner’s 7R, the seven types of cloud migration strategies are rehosting, refactoring, repurchase, retain, replatform, redeployment and retire.
1. Rehosting (“Lift and Shift”)
Rehosting, often referred to as “lift and shift,” is a cloud migration strategy in which existing applications and workloads are moved to the cloud without any changes or modifications.
This type of migration is best suited for applications that have been designed to run on cloud-native platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or IBM Cloud.
Benefits of Rehosting
The main benefit of rehosting is that it can be completed quickly and with minimal disruption to the application.
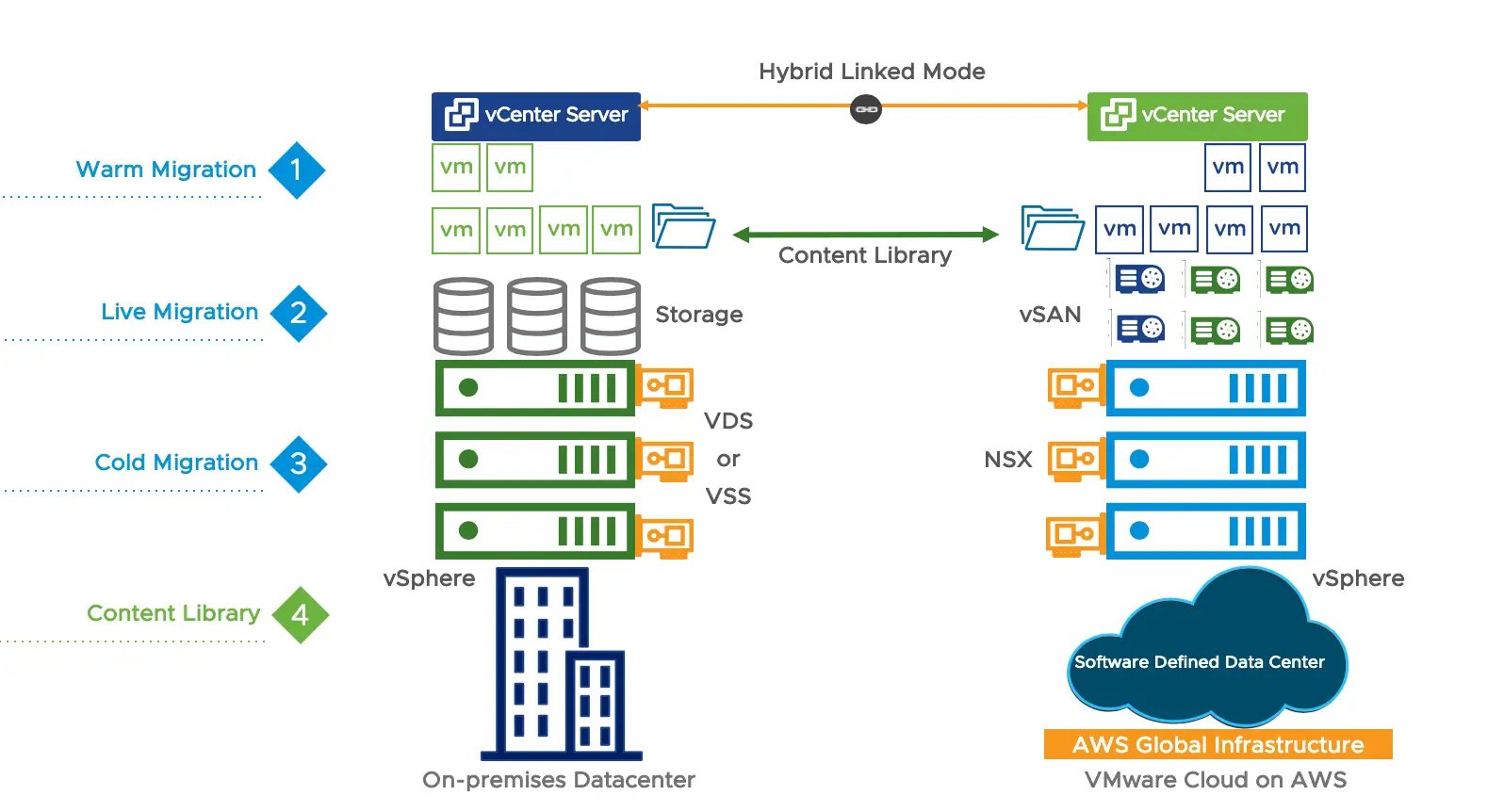
2. Refactoring
Refactoring is a cloud migration strategy in which existing applications and workloads are modified so that they can run more efficiently on the new cloud platform.
This type of migration is best suited for applications that require significant changes in order to be compatible with the target cloud platform.
Benefits of Refactoring
The main benefit of refactoring is that it can help to improve application performance and reduce costs by taking advantage of features offered by the target platform.
3. Repurchase
Repurchase is a cloud migration strategy in which existing applications and workloads are replaced with similar solutions from the target cloud platform.
This type of migration is best suited for applications that do not require significant changes in order to be compatible with the target platform but may need additional features or capabilities that are not available from the current solution.
Benefits of Repurchasing
The main benefit of repurchasing is that it can help businesses take advantage of features offered by the target platform while still maintaining compatibility with their existing systems.
4. Retain
Retain is a cloud migration strategy in which existing applications and workloads remain unchanged but are moved to the new cloud platform for better performance or cost savings.
This type of migration is best suited for applications where there are no significant changes required in order to be compatible with the target platform but where better performance or cost savings can be achieved by moving them to the new environment.
Benefits of Retaining
The main benefit of retaining existing applications and workloads is that it can help businesses take advantage of features offered by the target platform while also minimising disruption during the transition process.
5. Replatform
Replatforming is a cloud migration strategy in which existing applications and workloads are modified so they can take advantage of features offered by the target cloud platform, such as automation or scalability options, without requiring significant changes to their underlying architecture or codebase.
This type of migration is best suited for applications where there may be some minor modifications required but where most of its functionality remains unchanged after being migrated to the new environment.
Benefits of Replatforming
The main benefit of Replatforming is that it can help businesses quickly take advantage of features offered by their chosen cloud provider without needing extensive rewrites or refactoring work on their part.
6. Redeployment
Redeployment is a cloud migration strategy in which existing applications and workloads are packaged into containers so they can be deployed quickly on any public or private clouds without requiring significant changes to their underlying architecture or codebase.
This type of migration requires minimal effort on behalf of IT teams, since all components needed for deployment are already pre-packaged inside container images.
Benefits of Redeployment
The main benefit associated with redeployment lies in its ability to enable faster deployments across multiple clouds, making it an ideal choice for companies looking for flexibility when deploying their apps.
7. Retire
Retire refers to decommissioning an application once it has been migrated successfully onto another environment, either public or private, depending on what works best for your business.
Benefits of Retiring
Decommissioning an application ensures that resources previously allocated towards running this application will now become available, thus allowing you free up resources, save money, reduce complexity, etc.
Furthermore, this approach allows you access historical data stored within these retired systems if needed at any point down the line.
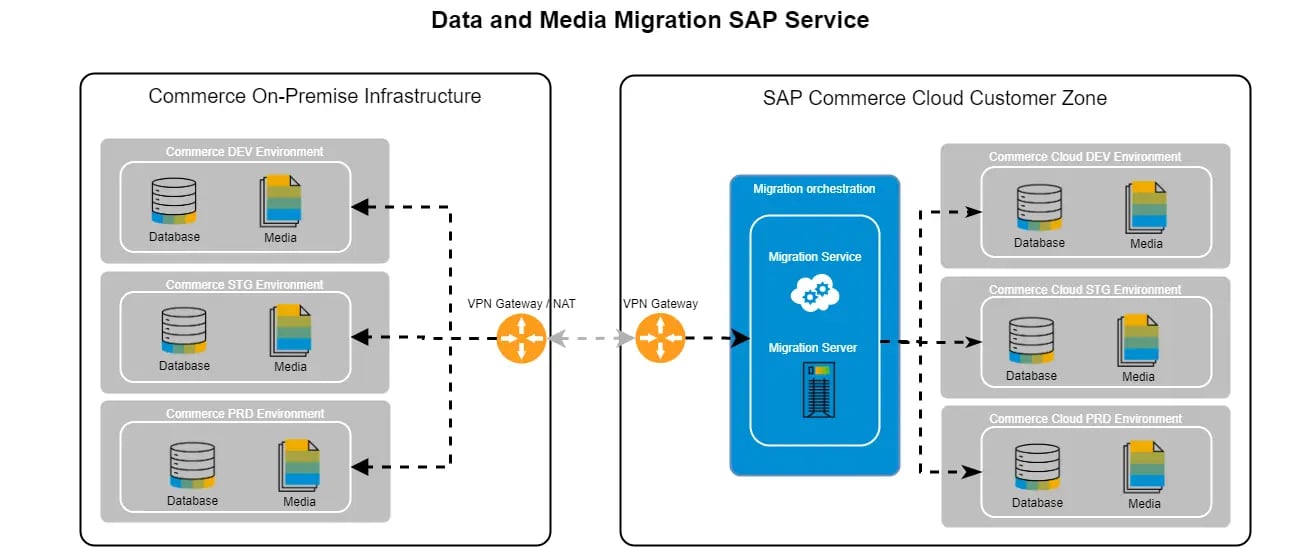
On Premise to Cloud Migration Steps
Here are the 9 steps for a successful on-premise to cloud migration:
Step 1: Assess Needs
The first step in a successful on premise to cloud migration is to assess your needs and determine what type of cloud service best suits them.
This includes evaluating the current infrastructure, applications, and data storage needs of the business.
It is important to consider scalability, cost, security, and other factors when making this decision.
Step 2: Plan Migration
Once the type of cloud service has been identified, the next on premise to cloud migration step is to plan out the migration process.
This includes creating a timeline for each task that needs to be completed as well as determining who will be responsible for each task.
Additionally, any necessary changes to existing processes or systems should be identified during this phase.
Step 3: Develop Strategy
The third step in a successful on-premise to cloud migration is to develop a strategy for migrating data and applications from the existing environment to the cloud service provider's platform.
This includes deciding which applications and data need to be migrated and how they will be migrated (e.g. using backup software or manual processes).
Step 4: Test Environment
Prior to commencing the cloud migration process, it is crucial to conduct thorough testing of the environment by simulating real-world scenarios.
This step allows for the identification of any potential challenges related to compatibility or performance that may arise during the actual migration process.
Step 5: Migrate Data/Applications
After testing has been completed, it’s time to begin migrating data and applications from the existing environment to the cloud service provider's platform.
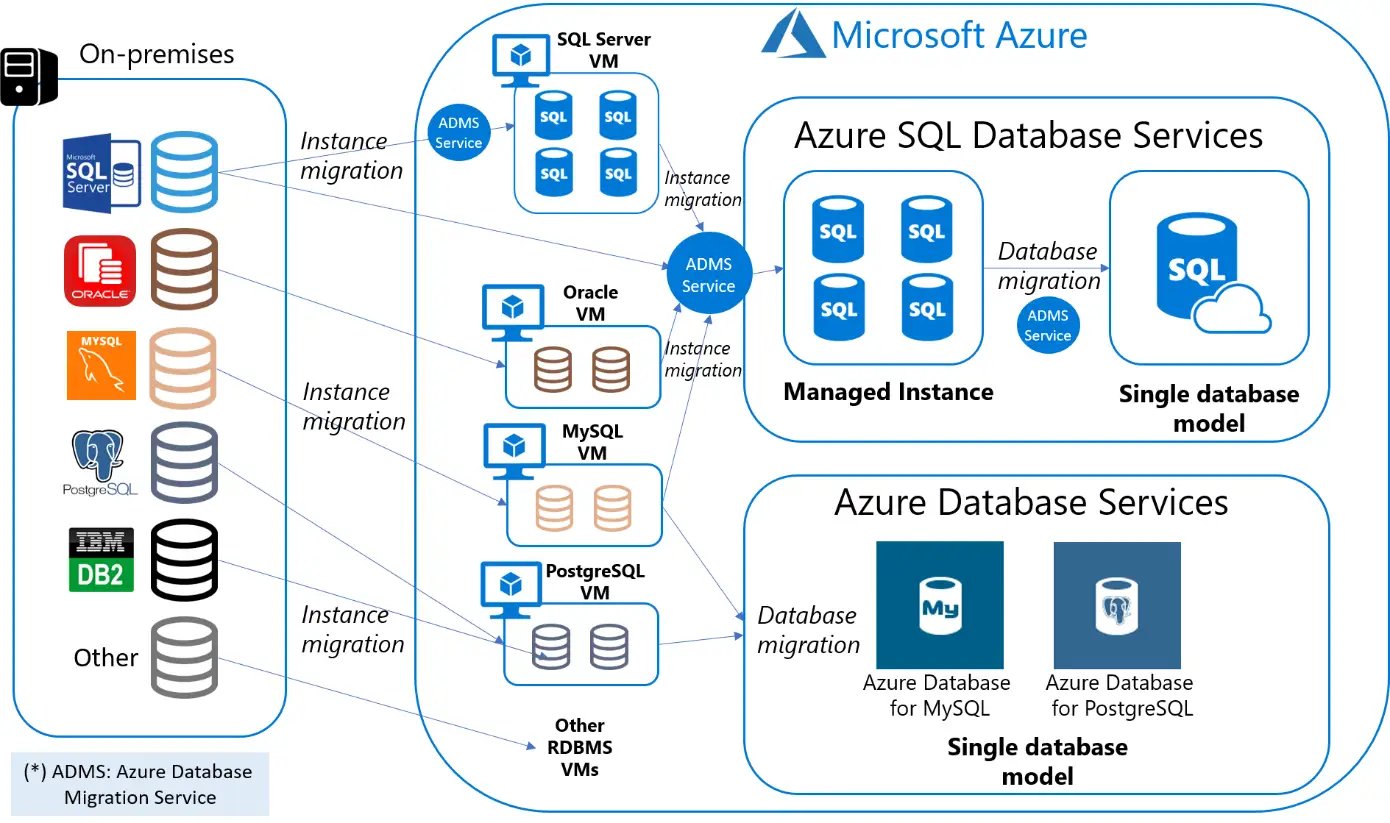
Depending on the magnitude of your organisation's data and applications, this process may require a significant amount of time.
Therefore, it is crucial to have ample resources allocated for the on-premise to cloud migration to guarantee a seamless and efficient transition, eliminating any potential setbacks or unforeseen challenges that may arise.
Step 6: Monitor Performance
Once all of your data and applications have been successfully migrated from on premise to cloud, it’s important that performance is monitored closely in order to ensure that everything is running smoothly on the new system as expected.
Moreover, it is crucial to consider mission-critical applications that are essential for the smooth operation of your business.
These applications must remain functional at all times, without any interruptions or unexpected downtime caused by technical issues with hardware or software components.
This applies to both your local network infrastructure and the remote cloud provider's environment.
Step 7: Establish Security Protocols
In order to ensure a successful transition from on-premise to cloud migration, it is crucial to establish robust security protocols that safeguard sensitive organisational data from unauthorised access.
These protocols should strike a balance between providing users with necessary access for job-related activities, such as remote login from home, while also maintaining strict security measures.
By implementing these security protocols, businesses can protect their valuable data and mitigate the risks associated with the migration process.
Step 8: Implement Backup Solutions
In addition to establishing robust security protocols for on premise to cloud migration, it is crucial to implement reliable backup solutions.
These backup solutions are not only essential for protecting against hardware failures, but also for safeguarding businesses against malicious attacks like ransomware.
Without proper backups in place, a single attack could potentially cripple an entire organisation.
Therefore, it is imperative to have robust backup systems established prior to any potential security breach or threat.
Step 9: Monitor Progress/Make Adjustments
Lastly, after successfully completing all migrations and providing comprehensive training to employees on the usage of their new systems, it is essential to maintain a proactive approach by regularly monitoring performance metrics.
This includes analysing uptime percentages and downtime percentages over specific time intervals (e.g. weekly, monthly, quarterly) to make necessary adjustments if required.
By comparing these results with the initial expectations set prior to the completion of migrations, businesses can ensure the ongoing success of their cloud migration journey.
Train your Employees
In order for an on-premise-to-cloud migration project to be successful, it is crucial to prioritise proper training for employees on how to effectively use the new system(s) once the migrations have been completed.
This involves ensuring that employees are fully aware of any changes that may have taken place in their individual roles during the transition period.
Additionally, they should be acquainted with any necessary modifications to their tasks, taking into account the variances between the pre-migration and post-migration environments.
It is especially important to address any variations in user interfaces between different systems architectures.
By providing thorough training, businesses can ensure a smooth and seamless transition for their employees during the migration process.
On premise to cloud migration challenges
Here are the challenges of cloud migration which should be addressed for a successful on premise to cloud migration, as a checklist:
Security Concerns
One of the biggest challenges associated with moving from an on-premise to a cloud environment is security concerns.
While cloud providers are typically very secure, there may be gaps in the security that can leave your data vulnerable to malicious actors.
Additionally, it can be difficult to ensure that all of your data is encrypted and secure when migrating to the cloud.
Cost Considerations
On-premise solutions can be expensive, but so can cloud solutions. When considering a move to the cloud, you need to consider not only the upfront costs but also any ongoing fees associated with storing and managing your data in the cloud.
Additionally, you need to factor in any additional costs such as training or software licenses that may be required for successful on premise to cloud migration.
Compatibility Issues
When moving from an on-premise solution to a cloud one, you may encounter compatibility issues between different versions of software or hardware platforms.
This can lead to delays in migration as well as potential data loss if not addressed properly prior to migration.
Data Migration Challenges
Data migration is one of the most challenging aspects of moving from an on-premise solution to a cloud environment.
You must ensure that all of your data is moved correctly and securely while also ensuring that none of it is lost during the process.
Additionally, you must make sure that all applications and services are compatible with the new environment before beginning migration.
Regulatory Compliance
When moving from an on-premise solution to a cloud environment, you must also consider any regulatory compliance requirements that may apply in order for your business operations to remain compliant with applicable laws and regulations.
Depending on where you are located, this could mean making sure that certain types of data are stored securely or ensuring that certain processes are followed correctly before migrating data offsite.
Change Management
Lastly, the management of change presents yet another hurdle in the journey from on-premise to cloud migration.
This task demands meticulous planning and seamless coordination among IT personnel and other key stakeholders within your organisation to ensure a smooth transition throughout the process.
On premise to Cloud Migration FAQs
What is the difference between cloud and on-premise migration?
The difference between cloud and on-premise migration is that cloud migration moves the IT infrastructure and data to remote servers hosted by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure. On the other hand, on-premise migration keeps the IT infrastructure and data on-site, hosted on company-owned servers.
How do I migrate from premise to Azure cloud?
For a successful migration from premise to Azure cloud, you’ll need to assess your current system, plan your migration, and execute your plan. The process can be simplified with some guidance from Microsoft's Azure migration experts.
How much does it cost to migrate from on-premise to cloud?
The cost of on-premise to cloud migration depends on several factors including the size of the business, the amount of data to be transferred, the complexity of the infrastructure, and the level of support required.
What is a key step in migrating an on-premises application to the cloud?
The key step in migrating an on-premises application to the cloud is to assess the compatibility of the application with the cloud. This means examining the application's architecture, dependencies, and data requirements to determine whether they can be supported in a cloud environment.
You can learn more with our 'Migrating to the Cloud' whitepaper, which you can find below:

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)






.png?width=536&name=Blog%20Hero%20Banners%20(13).png)

