Are your business teams at risk of falling victim to a phishing attack from IT scammers? It's more likely than you think.
In recent years, high-profile cybercrime scams have become increasingly common with hackers targeting organisations of all sizes across multiple sectors.
But one tactic is still surprisingly prevalent—impersonating IT support in order to commit fraud and gain confidential control over networks.
With businesses relying more heavily on digital operations in 2023, it's important that executives remain aware of this scam and have up-to-date knowledge of how to protect employees against it.
Let’s explore what phishing impersonation attack look like and how marketers, MDs , CEOs and CFOs can prevent them from making their way into the network.
Impersonation Attack Definition
An impersonation attack is a type of phishing cyber attack that involves a cyber criminal posing as an individual, system, or organisation to deceive the victim and gain unauthorised access to sensitive information.
Email impersonation attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated with the advent of social engineering tactics, such as phishing, vishing, and smishing.
Attackers may use a fake email address, website, secure connection, or even a phone call to impersonate and trick the victim into disclosing confidential data, installing malware, transferring funds, or performing other malicious actions.
To prevent impersonation attacks, it is crucial to verify the authenticity of all requests and communication, use multi-factor authentication, regularly update security software, and raise awareness about the dangers of social engineering.
Impersonation attack examples
An impersonation attack occurs when an attacker masquerades as a trusted entity to deceive people and gain access to sensitive data.
An example of an impersonation attack is a phishing email, in which the attacker poses as a legitimate company or organisation and tricks the recipient into clicking on a malicious link or entering their login credentials.
Impersonation attacks can also happen in person or over the phone, with the attacker pretending to be someone they're not to gain access or information.
As we become more dependent on technology, it's crucial to be aware of these types of attacks and take appropriate measures to protect ourselves and our sensitive information.
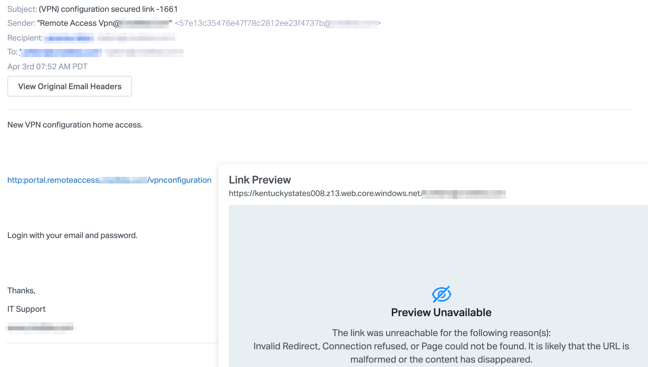
According to Abnormal Security, the attack impersonates a notification email from your IT support team - complete with a fake email impersonating the domain of your organisation.
The email includes a link to a 'New VPN configuration home access' and it specifies to login with your email and password, with the email signed off by "IT Support". If you click the link, you are redirected to an Office 365 credential phishing website.
The landing page is hosted on a Microsoft .NET platform and looks identical to the O365 login website, making it difficult for users to realise they're being scammed.
The phishing email includes a link that references the targeted organisation's name, which is used to gain the trust of the recipient and get them to lower their guard.
This type of attack is a simple way for cybercriminals to gain a user's information, and use that to gather data and access to your organisation.
Abnormal Security state that they have seen several versions of this attack across multiple clients from different senders and IP addresses, however, the same payload link was used, which indicates a single attacker controls the phishing landing page.
Types of impersonation attacks
Here are the 5 most common types of impersonation attacks:
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are one of the most common types of impersonation attacks. In this type of attack, a malicious actor sends emails or other messages that appear to be from a legitimate source to trick victims into revealing sensitive information or installing malicious software on their devices.
These emails often contain links to malicious websites or attachments containing malware.
2. Voice Impersonation Attacks
Voice impersonation attacks involve an attacker using a voice-altering device or software to imitate another person's voice to gain access to confidential information or systems.
These types of impersonation attacks is becoming increasingly common as technology advances and voice recognition systems become more sophisticated.
3. Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks involve an attacker using deception and manipulation techniques to gain access to confidential information or systems.
In these types of email impersonation attacks, the attacker may use tactics such as pretending to be someone else, creating false identities, or sending fake emails to convince victims to provide sensitive information or take certain actions that will benefit the attacker.
4. Identity Theft
Identity theft is another types of impersonation attacks where an attacker uses stolen personal information such as a social security number, credit card number, driver's license number etc, to commit fraud or other crimes in the victim's name.
Identity theft can have serious financial and legal consequences for victims, so it is important for them to take steps such as regularly monitoring their credit reports and changing passwords frequently to protect themselves from this type of attack.
5. Password Reuse Attacks
Password reuse attacks occur when attackers use stolen passwords that have been previously exposed through data breaches to gain access to accounts belonging to other users who have reused those same passwords across multiple sites and services.
These types of impersonation attacks can be avoided by using unique passwords for each account and regularly changing those passwords on a regular basis.
How to prevent impersonation attacks
Here are the 10 most effective ways to prevent impersonation attack:
1. Use a Strong Password
Using a strong and unique password is one of the best ways to prevent an impersonation attack.
A strong password should be at least 8 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
It's also important to make sure that your passwords are different for each account you use, as using the same password across multiple accounts can make it easier for attackers to gain access to your accounts.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) on all of your online accounts is another great way to protect yourself from impersonation attacks.
2FA requires users to enter both their username and password, as well as an additional code sent via text message or generated by an authenticator app.
This makes it much more difficult for attackers to gain access to your accounts, even if they have stolen your username and password.
3. Monitor Your Accounts Regularly
It's important to regularly monitor your online accounts for any suspicious activity or unauthorised changes.
Look out for strange logins from unfamiliar IP addresses, changes in contact information or passwords, or any other suspicious activity that could indicate an impersonation attack has taken place.
4. Avoid Public Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured and can be easily accessed by anyone in the vicinity, making them a prime target for attackers looking to launch impersonation attacks.
To keep yourself safe when using public Wi-Fi networks, avoid accessing sensitive information such as bank accounts or email addresses while connected to them, and always use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when possible.
5. Be Wary of Phishing Emails
Phishing emails are one of the most common types of email impersonation attacks used by attackers looking to gain access to personal information such as usernames and passwords through impersonation attacks.
Be wary of any emails that look suspicious or ask you for personal information such as usernames or passwords - these are likely phishing attempts trying to trick you into giving away your credentials so they can be used in an impersonation attack against you!
6. Educate Yourself on Cybersecurity Best Practices
Learning about cyber security best practices is one of the best ways you can protect yourself from becoming a victim of an impersonation attack or other forms of cybercrime.
Make sure you understand how attackers operate so that you can recognise potential threats before they become serious problems!
7. Use Email Security Software
Installing security software on all devices connected to the internet is another great way to protect yourself from becoming a victim of an impersonation attack or other forms of cybercrime.
Email Security software such as anti spam and antivirus programs can help detect malicious software before it has a chance to do any damage, while firewalls can help prevent unauthorised access from outside sources like hackers trying to gain access through an impersonation attack!
8. Double-Check the Sender
If you receive an unexpected email, make sure you double-check the sender's email address.
You can do this by hovering over the 'From/Sender' email address, or by clicking on it to reveal the real email address it's been sent from, not just the display name.
9. Double-Check URLs/Hyperlinks
If you've ever had to add a hyperlink into a document or email, you will know that any word can be turned into a hyperlink, even if you've copied and pasted a URL such as, 'www.google.co.uk' into an email, the hyperlink can be edited afterwards.
Therefore, make sure you check hyperlinks before clicking on them - you can do this by hovering over them in the email or if you did click on the link, check the address bar and do not enter your credentials if a website/URL looks suspicious.
10. Contact your IT department
If you've received an email and you're unsure whether it's safe to download attachments or click on links, get in touch with your IT support team.
It's better to be cautious than overly trusting, as one click can lead to malicious downloads and malware.
Our blog on phishing emails contains examples (with images) of what you should look out for and the warnings signs of phishing emails, including those that are highly targeted and personalised.
Email Protection
If you haven't set this up already, you should invest in Email Protection. Security risks to your emails are constantly evolving, which is why you need to have email protection software that'll defend against both known and new threats.
Find out more about email protection.
If you'd like to discuss how you can protect your organisation and your users from email impersonation attacks, please get in touch and we'd be happy to help.
We can provide training for your users as well as security solutions to help safeguard your data from cybercriminals.

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)






.png?width=536&name=Blog%20Hero%20Banners%20(5).png)
