While multi-factor authentication provides an extra layer of security for businesses, it also introduces a new risk of identity-based attacks known as MFA fatigue attacks.
Did you know that Microsoft's systems face over 1,000 password attacks every second? Yeah, it's crazy how relentless cyber threats can be. Even more important to note is that more than 99.9% of compromised accounts don't have MFA enabled.
Moreover, despite the implementation of Multifactor Authentication (MFA), a significant 28% of users continue to be targeted through various tactics, including SIM swapping, MFA fatigue attacks, and AiTM attacks.
For those who don’t know, multi-factor authentication is a way to secure your online accounts and data by requiring multiple forms of identification before granting access. Typically, this involves something you know, like a password, and something you have, like a smartphone or token device.
However, multi-factor authentication has its own set of risks. One of the risks is that it can be inconvenient for users to repeatedly provide multiple forms of identification, which can lead to frustration and non-compliance.
Additionally, the systems utilised for multifactor authentication can be vulnerable to hacking or other security breaches, which can compromise the sensitive information intended to be safeguarded.
In this blog post, we will discuss what an MFA fatigue attack is, how it works, signs to watch out for, and steps UK businesses can take to bolster their defences against this emerging threat.
Let us start by understanding what exactly MFA fatigue attacks are and how they work.
What is an MFA Fatigue Attack?
In simple terms, an MFA fatigue attack is a clever social engineering cyberattack technique in which attackers continuously bombard the target victim's email, phone, or registered devices with second-factor authentication requests.
In case you don’t get confused with other terms, MFA fatigue attacks are also known as MFA spamming, MFA bombing, prompt spamming, push spam, authentication bombing, MFA Hammering and even MFA brute-force attacks.
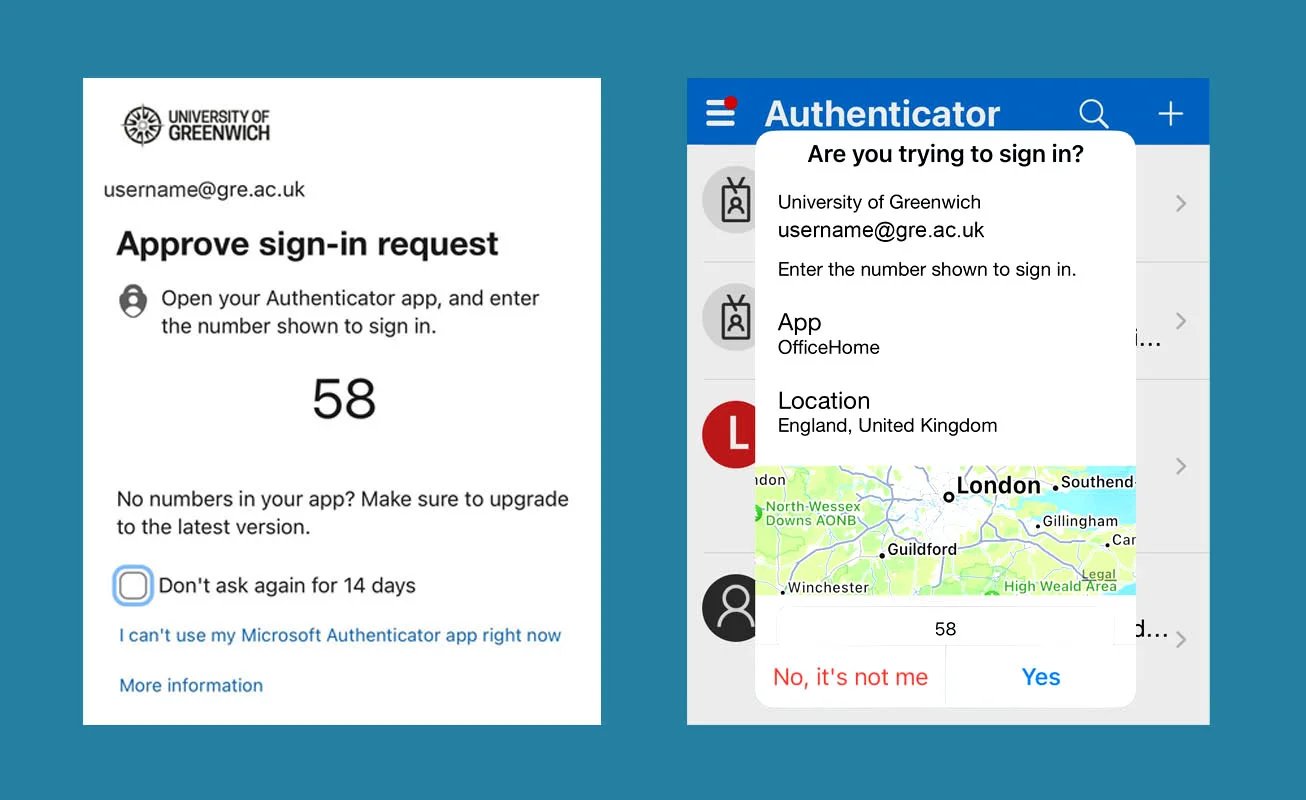 Source: University of Greenwich
Source: University of Greenwich
Now, you may be wondering why attackers would do this since you are using MFA, and they won't be able to bypass it. However, this is not always the case.
As per the Lapsus$ hackers’ group, the best time to trick the victim is at 1 am while they are trying to sleep. The victim would probably accept the request out of sheer frustration.
You can see in this below video, how the threat actors trick the victim.
Also, did you know that the attackers employ a clever phishing toolkit called EvilProxy? This toolkit utilises reverse proxy tactics to bypass multifactor authentication and steal MFA-protected credentials and session cookies.
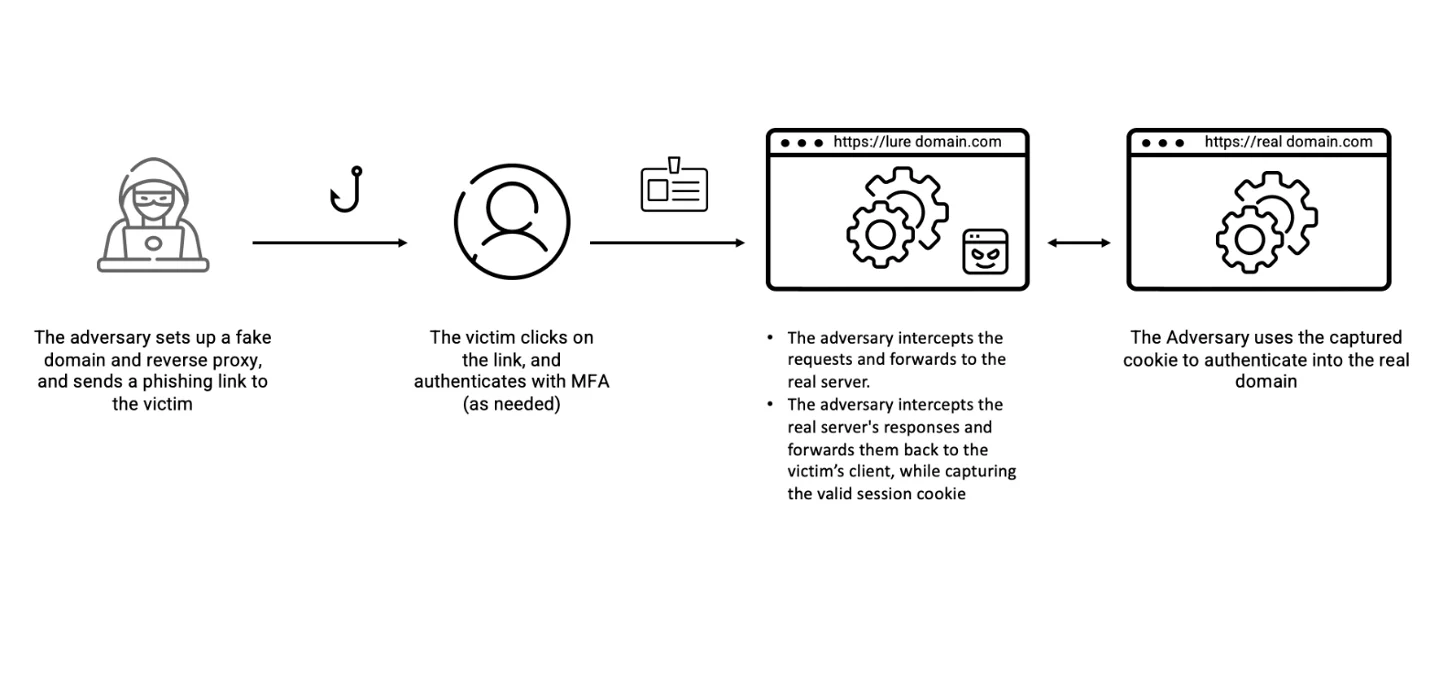
How does an MFA Fatigue Attack Start?
Here is the detailed four-step working process for MFA fatigue attacks:
Step 1: Threat Actor Gets Access to Your Login Credentials
Threat actors gain access to your login credentials through phishing emails, credential stuffing attacks, or purchasing user credentials on the dark web. Once they have your credentials, they can try to log in to your account or device.
If you have multi-factor authentication enabled, the attacker will be asked to provide a second-factor authentication code.
Step 2: The Attacker Will Send MFA Push Notifications
To carry out multi-factor authentication fatigue attacks, the attacker enters your email or phone number as the registered device for MFA push notifications. They then bombard your registered devices with a flurry of MFA requests, strategically overwhelming them and impairing your verification process.
This tactic also known as MFA bombing is used to hinder your ability to properly authenticate the requests.
Step 3: The Victim Receives Push Notifications Multiple Times
When targeted by an attacker, you might encounter multiple MFA requests in rapid succession. The attacker may use different social engineering tactics to create a sense of urgency, pressuring you into approving the requests promptly.
For example, they might falsely assert the presence of suspicious activity on your account or threaten to lock your account if the MFA request is not approved.
Step 4: Once the Victim Approves the Request, They Get ‘Fatigued’
If you fall for the attacker's tactics and approve MFA requests without properly verifying their legitimacy, the attacker gains access to your account or device. This can lead to the theft of sensitive information, fraudulent transactions, or the installation of malware on your device.
Now, you might be wondering how to find out if the MFA request is legitimate or fake. Here are some ways to help you identify whether an MFA fatigue attack is happening or not.
How can you identify if an MFA fatigue attack is occurring?
Here's how you can recognise if your multifactor authentication system is under attack:
- Unusual Frequency of Requests: You should keep an eye on the frequency of multifactor authentication requests. If there is a sudden surge in the number of authentication attempts, it could be a sign of a potential MFA fatigue attack.
- Geographical Anomalies: You should always monitor the geographical locations from which the requests are originating. A sudden change or a cluster of requests from unusual locations may indicate an MFA security threat.
- Atypical Access Times: You should always pay attention to the times when requests are being made. If there are authentication attempts during odd hours (late at night) or outside regular usage patterns, it might be a red flag.
- Device Discrepancies: Users should always analyse the devices used for authentication. A sudden increase in requests from unrecognised or suspicious devices may signal an MFA fatigue attack.
- Failed Authentication Patterns: You should track the number of failed authentication attempts. A pattern of repeated failures, especially from different sources, could be indicative of a coordinated attack.
- Anomalous User Behaviour: Always look for unusual user behaviour, such as multiple failed attempts followed by a successful one. This might suggest an attacker trying various methods to compromise the system.
- Monitoring System Logs: You must regularly review system logs and audit trails for any signs of unusual activity. Unexplained errors or anomalies in the logs could point to a potential attack.
How can you prevent becoming a victim of an MFA fatigue attack?
Here are 9 effective tips to prevent MFA fatigue attacks:
1. Choose Convenient MFA Methods
You can opt for MFA methods that are convenient and user-friendly, such as push notifications, biometrics (fingerprint or facial recognition), or hardware security keys. Avoid overly complex or time-consuming methods that can contribute to the MFA fatigue attacks.
2 . Use of Adaptive Authentication
Use adaptive authentication systems that can dynamically adjust the level of authentication required based on risk factors, user behaviour, and contextual information. This helps streamline the process for low-risk scenarios and strengthens it when necessary.
3. Educate Users on Security Awareness
Provide clear and concise training on the importance of multifactor authentication and the potential risks associated with MFA fatigue attacks. Help users understand the security benefits of multifactor authentication and how it protects them from unauthorised access.
4. Use Contextual Authentication Device
Implement contextual authentication, which considers factors such as the user's location, device, and network. This helps in tailoring the authentication process based on the context, reducing unnecessary challenges for users.
5. Implement Single Sign-On (SSO) Solutions
Implement Single Sign-On solutions to reduce the number of times users need to authenticate during a session. SSO allows users to log in once and access multiple applications without the need for repeated authentication.
6. Implement Fast Identity Online 2 (FIDO2) Authentication
FIDO2 solutions aim to address the limitations of traditional password-based authentication methods and provide a more secure and user-friendly approach to authentication with Web Authentication (WebAuthn) and Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP) security keys.
7. Use Risk-Based Authentication
Employ risk-based authentication mechanisms that assess the risk level associated with a specific login attempt. Higher-risk scenarios can trigger additional authentication factors, while lower-risk situations may involve fewer steps.
8. Customise Authentication Policies
Tailor MFA policies to suit the organisation's needs and the specific requirements of different user groups. Customisation allows for a more flexible and user-friendly approach to authentication.
9. Regularly Update Security Policies
Keep your security policies up to date, considering changes in technology, threats, and user preferences. Regularly reassess and adjust MFA measures to keep a balance between security and usability.
Recent Examples of MFA Fatigue Attacks
Some of the recent examples of MFA fatigue attacks claimed by the Lapsus$ group of attackers are:
Uber MFA Fatigue Attack
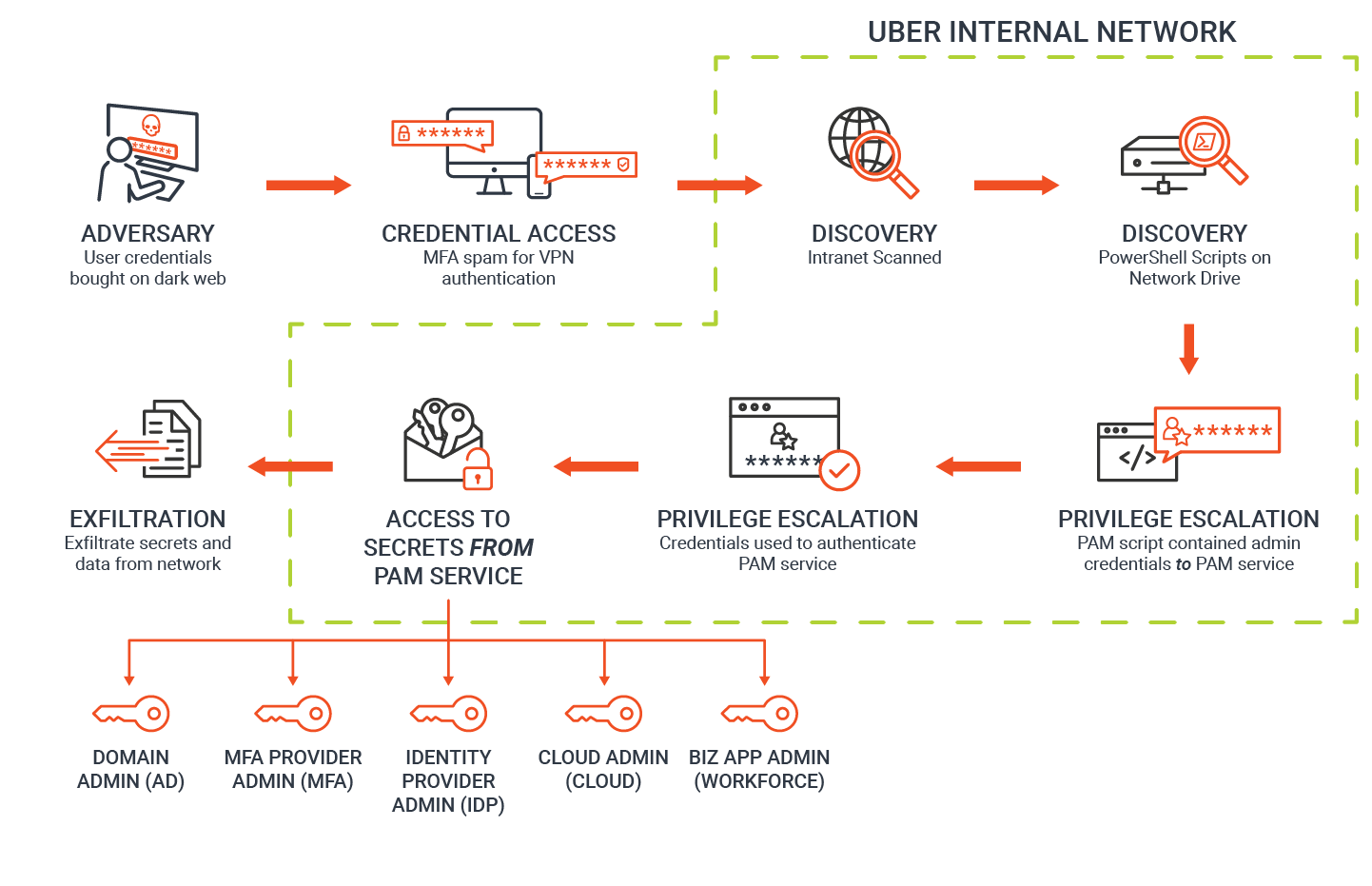
In September 2022, attackers managed to gain access to the VPN credentials of an external contractor, which were possibly stolen from the Dark Web. These attackers then made multiple attempts to log into the Uber account.
However, each time they tried to log in, they were met with a two-factor login approval request. Initially, the contractor blocked these requests.
However, the attackers then contacted the target via WhatsApp, pretending to be tech support. The attackers instructed the target to accept the Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) prompt, which ultimately allowed them to gain access.
Read the complete news here.
Cisco MFA Fatigue Attack
In May 2022, a Cisco employee's personal Google account was hacked. The attacker, believed to be a member of a ransomware gang, used "MFA fatigue" tactics to bombard the victim's device with numerous authentication push requests, hoping they would accidentally approve one.
The attacker also made voice-phishing calls, pretending to be a support provider for Cisco, to gain access to a corporate VPN account.
Once the victim approved an authentication request, the attacker added new MFA devices and infiltrated the Cisco VPN.
Read the complete news here.
Final Verdict
In conclusion, a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) fatigue, also known as MFA spamming, is a type of social engineering attack. The primary objective of this attack is to trick the victim into verifying their identity through a push notification to get access to their account and devices.
Also, the attack occurs mostly during night hours (around 1 a.m. as per the Lapsus$ group) because attackers target human factors like sleep time, frustration, and a sense of urgency.
However, you can protect yourself from an MFA fatigue attack by being vigilant. Watch out for unusual frequency of requests, pay attention to the time and location of the requests, analyse the device used for authentication, and check for any unusual user behaviour.
There are several ways to prevent an MFA fatigue attack, such as choosing a convenient MFA method, educating employees on security, implementing Single-Sign-On (SSO), implementing FIDO2 authentication, and disabling push notification as a verification method.
Remember, MFA is still the most effective way to keep your information safe.
If you have any questions about implementing any of these authentication methods, our cybersecurity experts are available to help you. Feel free to reach out to us or schedule a call for more information on MFA fatigue attacks.

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)






