Do you know the difference between cloud telephony and VoIP and which one to choose for your business communication? While they're both related, they're not quite the same thing.
Let's break it down in simple terms. VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol is all about making phone calls using the internet instead of traditional phone lines, while a cloud-based phone system uses VoIP phone calls but operates in the cloud-based systems.
This blog post will explore the key differences between cloud-based phone systems and voice-over-internet protocol communication tools.
Cloud Phone System vs VoIP: Key Differences
| Parameters | Cloud Telephony | VoIP |
| Infrastructure Location | Operates entirely in the cloud. | Can be implemented on-premises or in the cloud. |
| Ownership and Management | Managed and maintained by third-party service providers. | Responsibilities typically fall on the deploying organisation, whether on-premises or in the cloud. |
| Scalability and Flexibility | Offers high scalability and flexibility. Easily add or remove phone lines and features without significant hardware changes. | Scalability depends on on-premises hardware capacity or the scalability options provided by the chosen service provider. |
| Integration and Features | Comes with a wide range of integrated features such as auto-attendants, call routing, voicemail transcription, and integration with business applications. | Features and integrations may vary depending on the specific system deployed and the capabilities of the chosen service provider. |
| Cost Structure | Typically operates on a subscription-based model. | Cost structure varies based on deployment type (On-premises VoIP or cloud-based VoIP) |
What is Cloud Telephony?
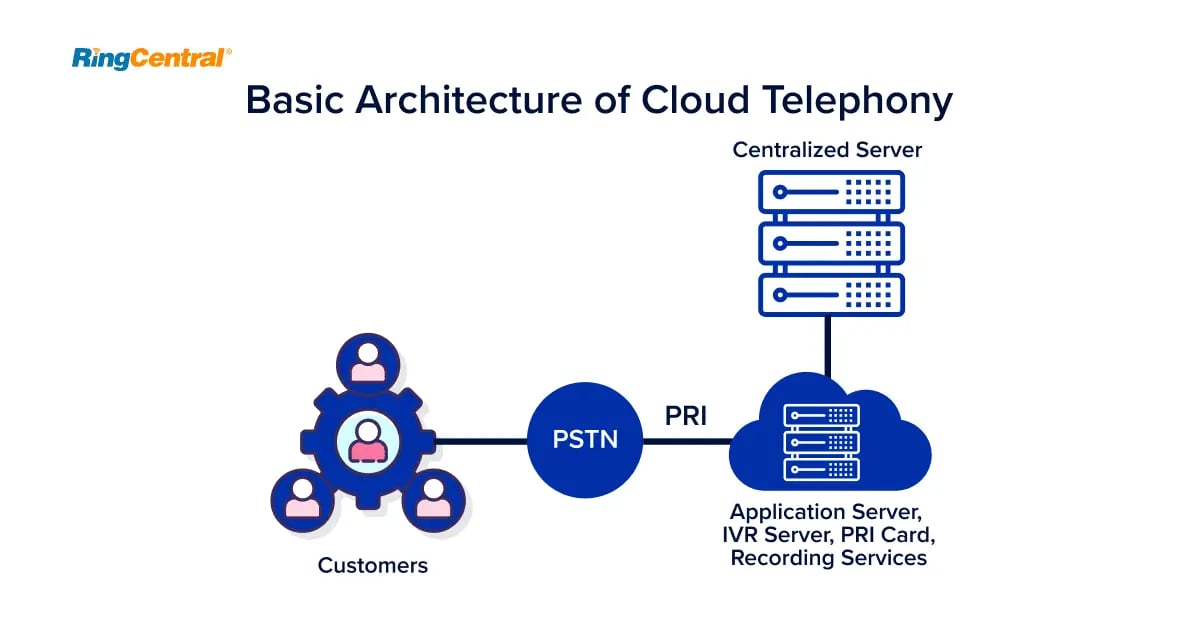
Cloud telephony, also known as cloud-based telephony or a cloud-based phone system, is a modern telecommunications technology that uses cloud computing to manage and handle voice communications over the Internet.
Unlike traditional phone systems that rely on physical infrastructure such as PBX (Private Branch Exchange) hardware installed on-premises, cloud phone systems operate entirely in the cloud, meaning that all voice data and call processing functions are hosted and managed by third-party service providers in remote data centres.
Some popular examples of cloud telephony services include RingCentral, Nextiva, Vonage, Gamma Horizon, and Google Voice.
How do Cloud Phone Systems Work?
Cloud phone systems are like talking on the phone, but it's all done over the internet. Your business phone system isn't in your office; it's stored in a virtual space called the cloud.
With VoIP magic integrated into unified communications, your voice becomes digital data and travels over the internet to reach the person you're calling.
What is Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)?
 Source: RingCentral
Source: RingCentralVoice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology that allows you to make voice calls using an internet connection rather than a traditional phone line.
Your voice is converted into digital data packets and transmitted over the internet to reach the person you're calling.
This means that you can make calls to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location, and often at a lower cost than traditional phone services. You can make calls from your computer, existing handsets, or other internet-connected devices without requiring multiple telephone lines.
VoIP is often used for long-distance and international calls because it eliminates the upkeep and maintenance cost of a PBX plain old telephone service.
Some common examples of VoIP services include Microsoft Teams, Skype, WhatsApp Calling, and Zoom.
How does VoIP work?
VoIP turns your voice signals into digital data, like converting your words into computer language. Instead of travelling through traditional phones, this digital data travels over a reliable internet connection to reach the person you're calling.
Your voice is broken down into tiny pieces called data packets. These digital packets are sent separately and then put back together at the other end. You can use special phones, and apps on your computer or mobile phones to make VoIP phone calls. They connect to the internet and handle the conversion of your voice into digital data.
VoIP systems route your calls through the internet to the right destination. It's like a digital switchboard directing your call to the correct person.
VoIP can be cheaper than traditional phone calls, especially for long-distance or international conversations because it uses a broadband internet connection instead of a dedicated telephone line.
What is the difference between cloud-based phone systems and VoIP?
Cloud-based phone systems and VoIP are often used interchangeably, but they differ in their underlying infrastructure and functionality.
While both cloud-based phone systems and business VoIP provide the same phone system functionality and utilise the internet for voice communication, cloud telephony typically involves hosted phone systems managed by third-party cloud providers, offering a range of features such as instant messaging, call analytics, virtual phone numbers and click-to-call functionality.
Many cloud-based phone systems include standard PBX features, but newer options eliminate the need for a physical desk phone.
On the other hand, VoIP focuses more on the technology itself, allowing users to make calls using internet-enabled devices without the need for traditional phones.
When comparing cloud phone systems with VoIP, it's important to understand that while they both involve the transmission of voice data over the Internet, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
Here's a breakdown of the differences between cloud-based system and VoIP:
1. Infrastructure Location
Cloud-based phone systems operate entirely in the cloud, meaning all call processing, management functions and data storage are hosted remotely by third-party providers.
On the other hand, VoIP can be implemented on-premises or in the cloud. On-premises VoIP systems require physical hardware installation, while cloud VoIP relies on internet-based infrastructure.
2. Ownership and Management
Cloud phone systems are managed and maintained by third-party service providers, reducing the need for businesses to own and manage telephony infrastructure.
In VoIP, the ownership and management responsibilities typically fall on the business deploying the VoIP system, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-based phone systems offer high scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to easily add or remove new users, phone lines and features as needed without significant physical hardware changes.
The scalability of a VoIP system depends on the capacity of the office premises hardware or the scalability options provided by the chosen VoIP service provider.
4. Integration and Features
Cloud systems come with a range of advanced features such as IVR (Interactive Voice Response), call routing, call recording, voicemail-to-email, and call analytics. These features are usually managed through a web-based interface with remote servers.
VoIP systems offer basic calling features like call forwarding, call waiting, and voicemail, but they may lack some of the advanced features available in cloud telephony platforms. However, VoIP systems can be customised and expanded with additional features through integrations and third-party applications.
5. Cost Structure
Cloud telephony services typically operate on a subscription-based model, where businesses pay a recurring fee for access to the service. This can include costs for usage, additional features, and support.
The cost structure of VoIP technology can vary depending on whether it's deployed on-premises or in the cloud. On-premises deployments involve additional hardware system and software costs, with ongoing maintenance costs. Cloud-based VoIP services often have a subscription-based pricing model similar to cloud telephony.
Summary
In summary, while cloud telephony and VoIP involve voice communication over the Internet, they differ in infrastructure, scalability, features, and cost structure.
In a nutshell, the primary difference between Cloud Telephony and VoIP lies in their infrastructure. Cloud Telephony operates through internet-hosted solutions, while VoIP involves transmitting voice calls over the internet.
Cloud phone system is a broader concept that encompasses VoIP but also includes additional services and functionalities typically provided through cloud systems.
Businesses should consider their communication needs, scalability requirements, and budget constraints when choosing between the two options. Contact Aztech for more information.
FAQs
What is the difference between VoIP and telephony?
Traditional telephony relies on physical phone service for voice communication, whereas VoIP utilises the Internet. VoIP offers greater flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability compared to traditional telephony.
What is the difference between cloud-based PBX and VoIP?
Cloud-based PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a type of cloud telephony service that includes features such as call routing, voicemail, and multi-party conferencing.
On the other hand, VoIP is a technology that enables voice calls to be transmitted over the Internet.
Is VoIP Calls Secure?
As a VoIP subscriber, you can use encryption protocols like Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure VoIP calls from security breaches.
Additionally, implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regularly updating software can enhance the security of VoIP systems.

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)







